Introduction to Common Microbial Culture Media (I)
Culture medium is a kind of mixed nutrient matrix artificially prepared from various substances according to the needs of various microbial growth, which is used to culture or separate various microorganisms. Therefore, the nutrient matrix should contain nutrients (including carbon source, nitrogen source, energy, inorganic salt, growth factors) and water that can be used by microorganisms. Depending on the type of microorganisms and the purpose of the experiment, there are different types and preparation methods of culture media.
Some common culture media in the experiment are introduced as follows:
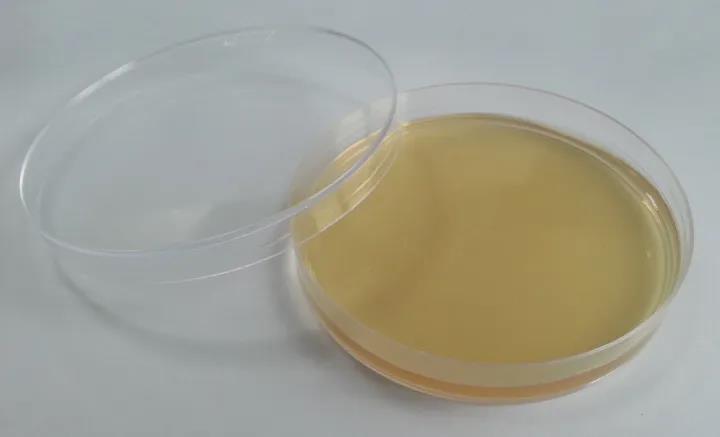
Nutritional agar medium:
The nutrient agar medium is used for the propagation and culture of common bacteria, for the determination of total bacterial count, preservation of bacterial species and pure culture. The main ingredients are: beef extract, yeast extract, peptone, sodium chloride, agar powder, distilled water. Peptone and beef powder provide nitrogen, vitamin, amino acid and carbon sources, sodium chloride can maintain balanced osmotic pressure, and agar is the coagulant of the culture medium.
Nutritional agar is the most basic type of culture medium, which contains most of the nutrients required for microbial growth. Nutritional agar can be used for routine bacterial culture.
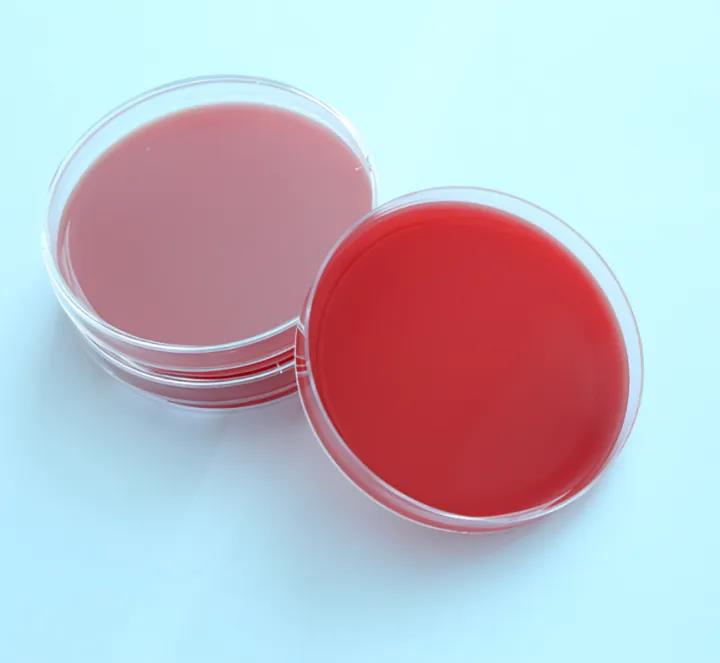
Blood agar medium:
Blood agar medium is a kind of beef extract peptone medium containing defibrinated animal blood (generally rabbit blood or sheep blood). Therefore, in addition to various nutrients required for cultivating bacteria, it can also provide coenzyme (such as factor V), heme (factor X) and other special growth factors. Therefore, blood culture medium is often used to cultivate, isolate and preserve certain pathogenic microorganisms that are demanding for nutrition.
In addition, blood agar is usually used for hemolysis test. During the growth process, some bacteria can produce hemolysin to break and dissolve red blood cells. When they grow on the blood plate, transparent or translucent hemolytic rings can be observed around the colony. The pathogenicity of many bacteria is related to hemolytic characteristics. Because the hemolysin produced by different bacteria is different, the hemolytic capacity is also different, and the hemolysis phenomenon on the blood plate is also different. Therefore, hemolysis test is often used to identify bacteria.
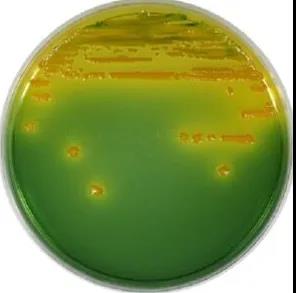
TCBS medium:
TCBS is thiosulfate citrate bile salt sucrose agar medium. For selective isolation of pathogenic vibrio. Peptone and yeast extract are used as basic nutrients in the culture medium to provide nitrogen source, carbon source, vitamins and other growth factors required for the growth of bacteria; The higher concentration of sodium chloride can meet the needs of halophilic growth of vibrio; Sucrose as fermentable carbon source; Sodium citrate, high pH alkaline environment and sodium thiosulfate inhibit the growth of intestinal bacteria. Cow bile powder and sodium thiosulfate mainly inhibit the growth of gram-positive bacteria. In addition, sodium thiosulfate also provides a sulfur source. In the presence of ferric citrate, hydrogen sulfide can be detected by bacteria. If there are hydrogen sulfide producing bacteria, black sediment will be generated on the plate; The indicators of TCBS medium are bromocresol blue and thymol blue, which are acid base indicators. Bromocresol blue is an acid-base indicator with a pH change range of 3.8 (yellow) to 5.4 (blue-green). There are two discoloration ranges: (1) the acid range is pH 1.2~2.8, changing from yellow to red; (2) The alkali range is pH 8.0~9.6, changing from yellow to blue.
TSA cheese soybean peptone agar medium:
The composition of TSA is similar to that of nutrient agar. In the national standard, it is usually used to test settling bacteria in clean rooms (areas) of the pharmaceutical industry. Select the test point in the area to be tested, open the TSA plate and place it at the test point. Samples shall be taken when exposed to air for more than 30min for different times, and then cultured for colony counting. Different cleanliness levels require different colony counts.
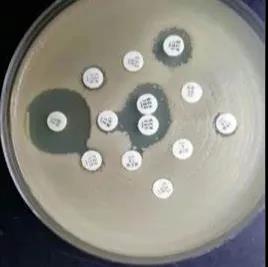
Mueller Hinton agar:
M-H medium is a microbial medium used to detect the resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics. It is a non selective medium on which most microorganisms can grow. In addition, starch in the ingredients can absorb toxins released by bacteria, so it will not affect the results of antibiotic operation. The composition of M-H medium is relatively loose, which is conducive to the diffusion of antibiotics, so that it can show obvious growth inhibition zone. In China’s health industry, M-H medium is also used for drug sensitivity test. When conducting drug sensitivity test for some special bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, 5% sheep blood and NAD may be added to the medium to meet different nutritional requirements.
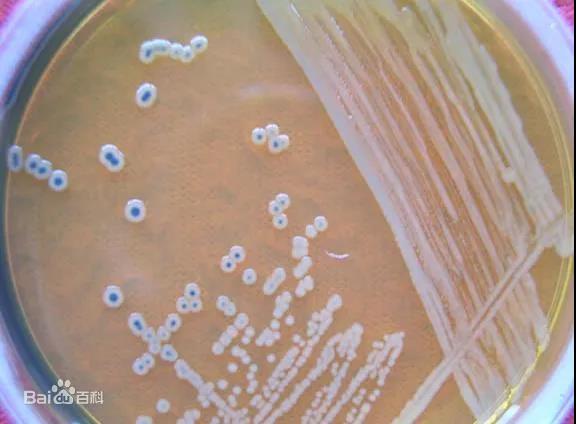
SS agar:
SS agar is usually used for selective isolation and culture of Salmonella and Shigella. It inhibits gram-positive bacteria, most coliforms and proteus, but does not affect the growth of salmonella; Sodium thiosulfate and ferric citrate are used to detect the generation of hydrogen sulfide, making the colony center black; Neutral red is the pH indicator. The acid producing colony of fermenting sugar is red, and the colony of non fermenting sugar is colorless. Salmonella is colorless and transparent colony with or without black center, and Shigella is colorless and transparent colony.
Post time: Jan-04-2023